With the Reverse Engineer Wizard in Microsoft Visio Professional and Premium editions, you can create a database model from an existing database, whether local or remote. This article will look at a connection to a remote Oracle database through Visio.
Database models graphically show the structure of a database so you can see how database elements, such as tables and views, relate to each other without showing the actual data. This can streamline creating a new database or understanding the structure of an existing one as well as assist developers/DBA with the process of managing or developing data dictionary for their databases.
Here are some of the database objects that Visio can generate through its reverse engineer feature by extracting the codes and properties:
•Tables
•Views
•Primary keys
•Foreign keys
•Indexes
•Triggers (including code)
•Check clauses (including code)
•Stored procedures (including code)
Step 1: Install Oracle 11g Client software on your server.
Download the Client software here
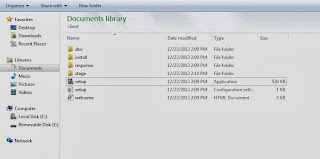
unzip the software
launch the installer by clicking “setup” in the client folder
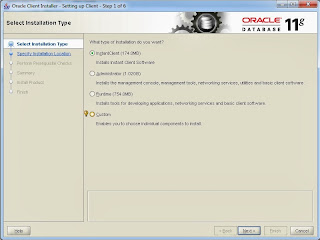
Select the installation mode you desire.
Step 2: Create a Local Service Name for the remote Database.
The next step is to create a Local Service Name (TNSnames.ora) for the remote database you will be connecting into. Oracle uses TNSnames.ora file as a window to connect to the remote server. Consequently, the TNSnames.ora file contains the connection properties like: (1) the remote server name/IP address (2) the SID, service or instance name (3) the port number (4) the protocol for communication with the server.
Launch "NETCA" from the command line to configure TNSnames.ora file
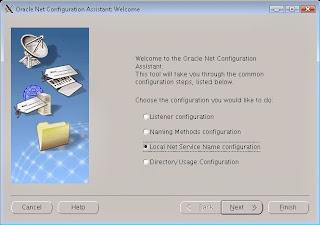
Choose Local Service Name configuration
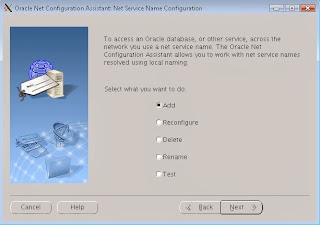
Select "add"
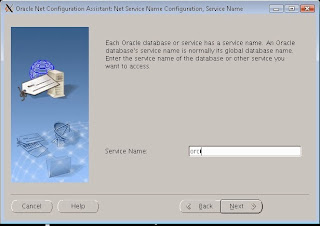
Type in the Oracle SID or service or instance name of the remote database
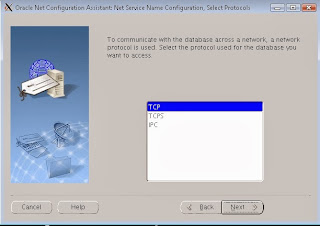
Select the protocol
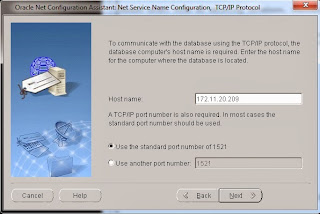
Type in the remote server name or IP address and the port number
To verify that the TNSnames has been correctly configured, from your local machine log in using the network:
sqlplus sys/****@orcl as sysdba
sqlplus system/****@orcl
You should be able to log into the remote database using the above command. If you can't, please repeat step 2 until you can connect.
Step 3: Connect the remote database to Visio.
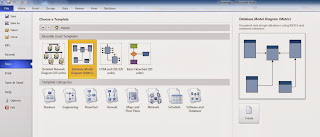
Once you launch Visio, click on "New" and search for "Database Model Diagram"
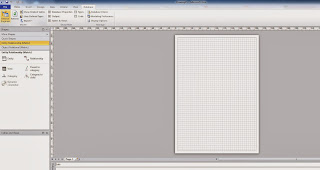
Click on Database menu and "Reverse Engineer"
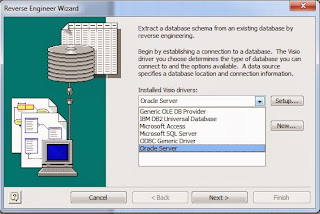
From the list of drivers, choose "Oracle Server"
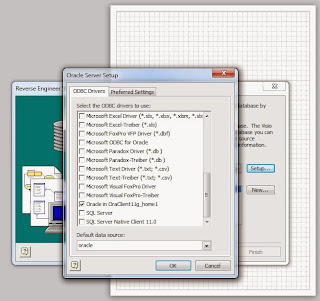
Click on "Setup" and check your "ORACLE_HOME" from the list
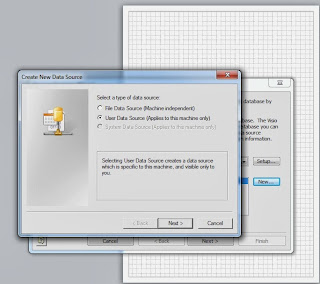
Click on "New" and select user data source
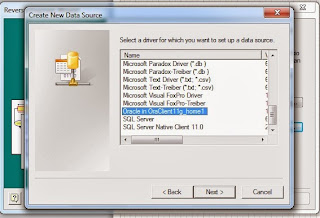
Locate your "ORACLE_HOME" from the list
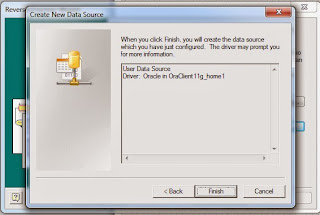
Click "Finish"
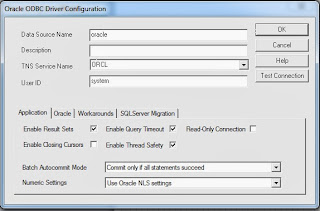
Choose the service name or SID from the list. You should have a dropdown containing the SID you configured. You can also test the connection to the remote server from this point.
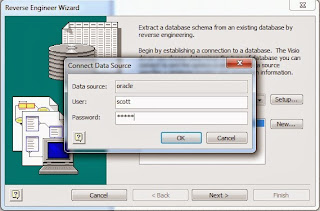
Using the right credential for the remote database, log in with "username" and "password".
You should be able to extract schema objects from your remote database if you follow these steps!
Thanks for reading.






